
B. Sc. II Animal Diversity IV (Old) Histology of Mammal By. Dr. Vidhin Kamble Sangola
T.S. of Ovary of Mice. An ovary is a germinal epithelium bounded by a solid structure covered by a thick layer of fibrous tissue known as tunica albuginea. It consists of an inner medulla and an outer cortex. The medulla comprises several round or oval bodies known as ovarian follicles. Follicle development takes place in the following stages:

Mammalian ovary and graafian follicles, light micrograph Stock Image C047/6173 Science
T.S. of Ovary (i) In the section of ovary, there is a mass of tissue lined with germinal epithelium. Inside that you will Graafian Follicle observe an ovum, which is a cell surrounded by one to several layers of follicular cells. As the ovum matures, the number of surrounding follicular cell layer increases (Fig. 4.2).

Professor Olexik Ovaries, Human anatomy and physiology, Reproductive system
B. Slide showing T.S of mammalian ovary Comments It is bounded by germinal epithelium flowed by thick layer of fibrous tissue, the tunica albuginea. Stroma is formed of connective tissue, interspersed with blood vessels, nerve fibers and spindle shaped cells. A primary follicle consists of a central ovum surrounded by a group of follicular cells.

Ovary Diagrams to Print 101 Diagrams
1. An ovary is a germinal epithelium bounded by a solid structure covered by a thick layer of. fibrous tissue known as tunica albuginea. 2. It consists of an inner medulla and an outer cortex. 3. The medulla comprises several round or oval bodies known as ovarian follicles. 4. Follicle development takes place in the following stages:

How to draw T.S. of ovary । structure of mammalian ovary । Biology class 12 YouTube
T.S. of Mammalian Ovary A mammalian ovary is a solid structure bounded germinal epithelium followed by a thick layer of fibrous tissue called tunica albuginea. The ovary consists of the outer cortex and inner medulla. The medulla consists many rounded or oval bodies called ovarian follicles at various stages of development.

Ovario Normal, Desarrollo Folicular Y Ovulación Stock de ilustración Ilustración de normal
In mammals, the blastula forms the blastocyst in the next stage of development. Here the cells in the blastula arrange themselves in two layers: the inner cell mass and an outer layer called the trophoblast. The inner cell mass is also known as the embryoblast; this mass of cells will go on to form the embryo..
Mammalian Ovary Under A Microscope Stock Image 243085597
1. The medulla 2. The cortex Medulla The medulla, also known as the zona vasculosa, is the deeper core region of the ovary. It has a stroma made up of loose connective tissues. Near the hilum, it comprises blood arteries, lymphatics, nerve fibres, and bundles of smooth muscle fibres. Cortex

Ovaries Function, Location, Hormones Produced. What control it?
Some species reproduce only once during their life span, whereas others, such as mammals, have reproductive cycles that are hormonally regulated; the female ovary is central to the process of reproduction and produces germ cells, as well as gonadal hormones. Keywords Corpus Luteum Follicular Fluid Zona Pellucida Meiotic Division Primordial Follicle

Ovary from cat (100 X)
Although the testis and ovary are functionally analogous and arise from a common primordial structure, the genital ridge, they are remarkably different organs, and their development is driven by distinct programs of gene regulation and cellular organization.

OvaryFollicles400x A&P.6.Continuity Pinterest
5 - The ovary. Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2012. In the mature animal the structure and function of the ovary is continually changing. Gonadotrophins secreted by the anterior pituitary gland stimulate the growth of Graafian follicles (folliculogenesis), ovulation, and the formation of corpora lutea.

Ts of ovary Biology 12468417
Solution 1 Externally, each testis is covered by three layers. These are: a. Tunica vaginalis: It is the outermost incomplete peritoneal covering made up of connective tissue and epithelium. b. Tunica albuginea: It is the middle layer formed by fibrous connective tissue. c. Tunica vasculosa:
[Solved] Mammal Ovary Follicles Need Labeling Primary follicle Secondary... Course Hero
An ovary is a germinal epithelium bounded by a solid structure covered by a thick layer of fibrous tissue known as tunica albuginea. It consists of an inner medulla and an outer cortex. The medulla comprises several round or oval bodies known as ovarian follicles. Follicle development takes place in the following stages:
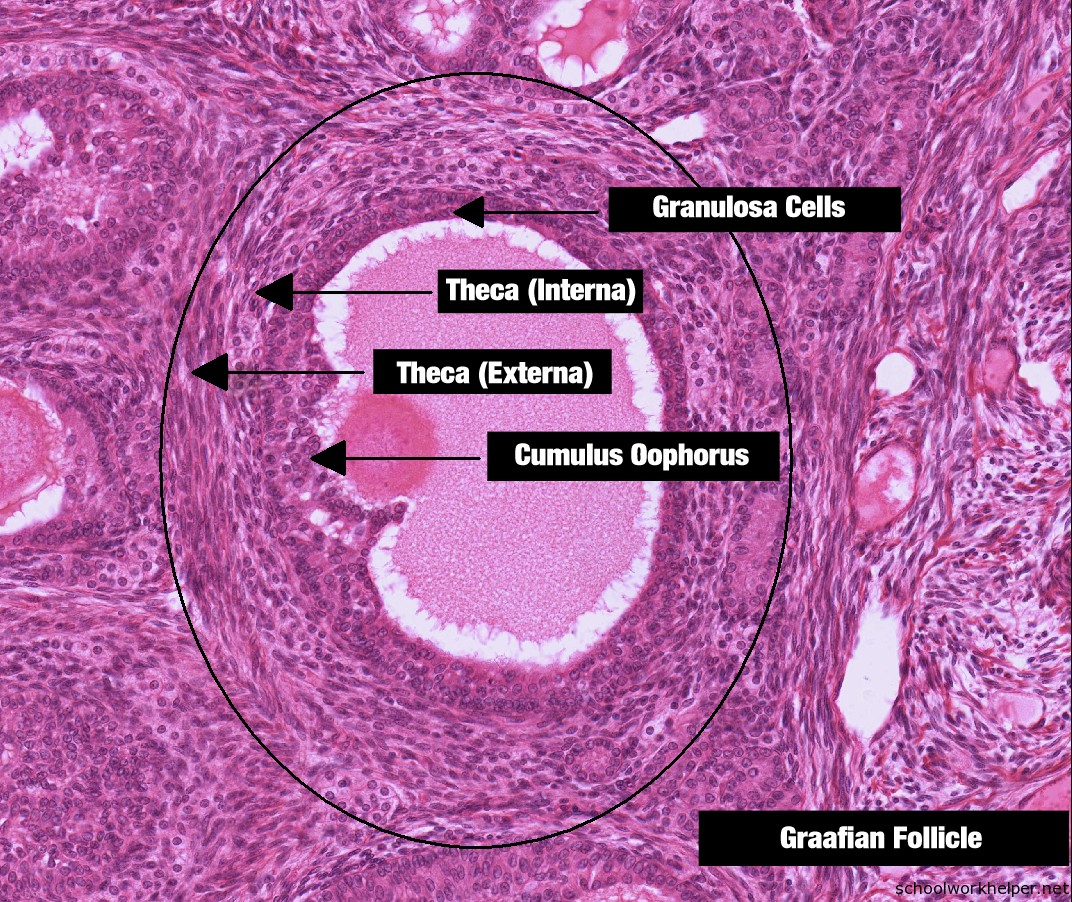
Ovarian Follicles Slide
Most mammals, including female humans, possess two ovaries, right and left. The development of gametes inside ovaries is called oogenesis. TS of mammalian ovaries will help you to study the several components of ovaries. Observation. There is a mass of tissue lined with germinal epithelium in the ovarian region.

Pin by Ali Mortza on histology Histology slides, Medical studies, Science equipment
T.S. of Mammalian Ovary. The mammalian ovaries are the reproductive organ in females inside which sex cells like eggs or ova are produced. In addition to the sex cells, the ovaries come in pairs and produce Oestrogen and Progesterone hormones that trigger reproduction in females. While ovaries are the primary reproductive organs in females, males have testis as their primary reproductive organ.

Diagrammatic Sectional View Of Ovary Labelled Diagram Of Ovary Class 12 Biology YouTube
Both functions of the mammalian ovary, the endocrine and (synthesis and secretion of steroid hormones) and exocrine (production of ova), depend upon the presence and cyclic growth of follicles, as the depletion of primordial follicles from the ovary leads to cessation of these f-unctions or female reproduction in mammals, or to postmenopausal period in humans.

TS of ovary, demonstrating stage II of maturity. Showing type three of... Download Scientific
Abstract. The prevailing concept of ovarian morphology, at the turn of the century, was that the important functional components were the follicles, especially the oocyte, and the corpora lutea. If one scans the voluminous literature that has accumulated during the past 45 years, one will find that the follicles and the corpora lutea still.