
calculus The derivative of a moving L2 norm Mathematics Stack Exchange
The Gateaux derivative of k · k at vin direction of uis defined as lim t→0 kv+tuk −kvk t. We say k · k is Gateaux differentiable at 0 6= vif and only if for all u∈ V, lim t→0 kv+tuk−kvk t exists. A concept related to the Gateaux derivative of norm function is the subdifferential set of norm function (see [9]). The subdifferential set
Where's my mistake? Manual Derivative of Layer Norm seems to not allow
However, it is far easier to differentiate this function by first rewriting it as f(x) = 6x − 2. f′ (x) = d dx( 6 x2) = d dx(6x − 2) Rewrite 6 x2 as 6x − 2. = 6 d dx(x − 2) Apply the constant multiple rule. = 6( − 2x − 3) Use the extended power rule to differentiate x − 2. = − 12x − 3 Simplify. Exercise 3.3.8.

(PDF) Some estimates of an integral in terms of the L^pnorm of the
Symbolab is the best derivative calculator, solving first derivatives, second derivatives, higher order derivatives, derivative at a point, partial derivatives, implicit derivatives, derivatives using definition, and more. Is velocity the first or second derivative? Velocity is the first derivative of the position function.
[Solved] Derivative of the squared L^2 norm of a 9to5Science
The concept of logarithmic derivative μ [ A] is used in [2], [1] in the theory of ordinary differential equations to obtain new results, e.g., in stability problems, and the results improve those obtained by using the norm ∥ A ∥.
Derivative of norm of function w.r.t realpart of function
Definition 4.3. A matrix norm ��on the space of square n×n matrices in M n(K), with K = R or K = C, is a norm on the vector space M n(K)withtheadditional property that �AB�≤�A��B�, for all A,B ∈ M n(K). Since I2 = I,from�I� = � �I2 � � ≤�I�2,weget�I�≥1, for every matrix norm.
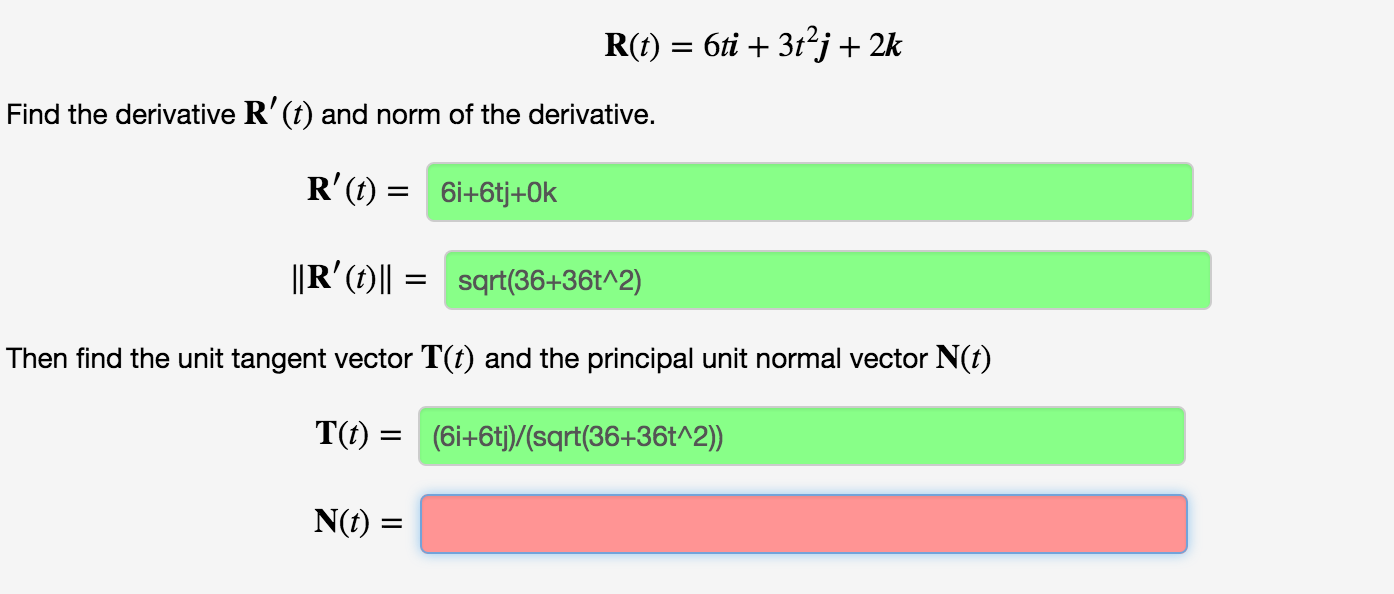
Solved Find the derivative R'(t) and norm of the derivative.
Subject classifications. Let X and Y be Banach spaces and let f:X->Y be a function between them. f is said to be Gâteaux differentiable if there exists an operator T_x:X->Y such that, for all v in X, lim_ (t->0) (f (x+tv)-f (x))/t=T_xv. (1) The operator T_x is called the Gâteaux derivative of f at x. T_x is sometimes assumed to be bounded.
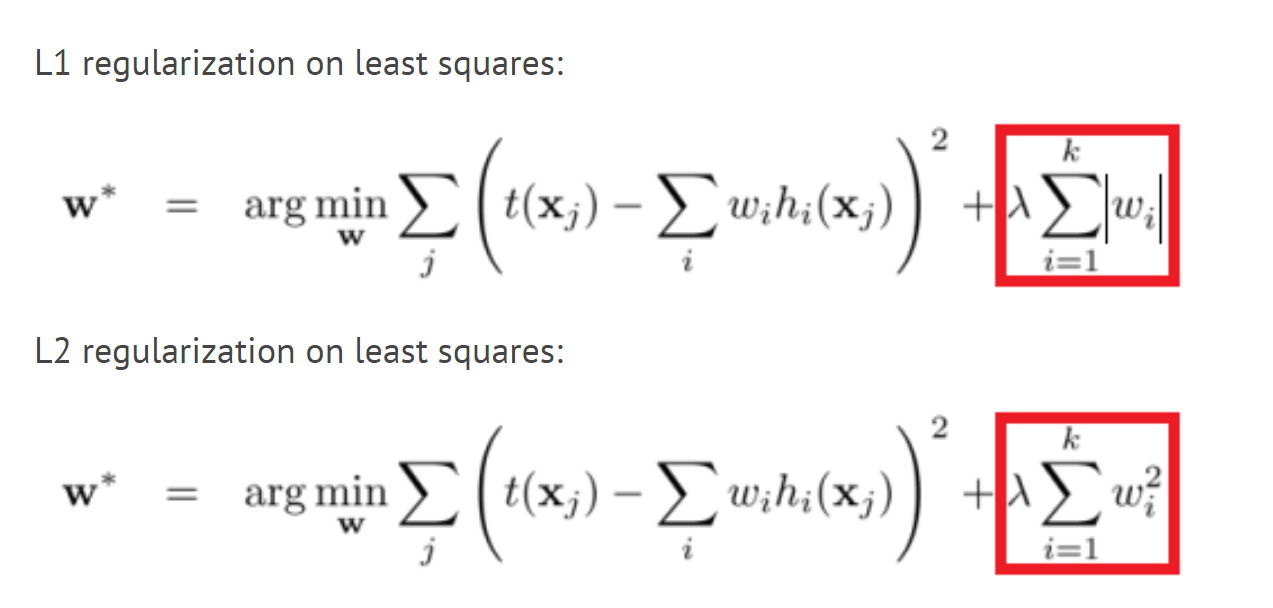
Only Numpy Implementing Different combination of L1 /L2 norm
The norm is extensively used, for instance, to evaluate the goodness of a model. By the end of this tutorial, you will hopefully have a better intuition of this concept and why it is so valuable in machine learning. We will also see how the derivative of the norm is used to train a machine learning algorithm.

linear algebra 2norm of a diagonal matrix and its relation to
Derivative of the 2 -norm of a multivariate function Ask Question Asked 10 years, 11 months ago Modified 3 months ago Viewed 92k times 33 I've got a function g(x, y) = ‖f(x, y)‖2 and I want to calculate its derivatives with respect to x and y. Using Mathematica, differentiating w.r.t. x gives me f ′ x(x, y)Norm ′ (f(x, y)), where Norm is ‖ ⋅ ‖.

linear algebra Derivatives Across Summations Mathematics Stack Exchange
Differential Integral Series Vector Multivariable Advanced Specialized Miscellaneous v t e The derivative is a fundamental tool of calculus that quantifies the sensitivity of change of a function 's output with respect to its input.

Matrix Norms YouTube
The max-absolute-value norm: jjAjj mav= max i;jjA i;jj De nition 4 (Operator norm). An operator (or induced) matrix norm is a norm jj:jj a;b: Rm n!R de ned as jjAjj a;b=max x jjAxjj a s.t. jjxjj b 1; where jj:jj a is a vector norm on Rm and jj:jj b is a vector norm on Rn. Notation: When the same vector norm is used in both spaces, we write.

L2norm of the error for the derivative x u ∂ ∂ / . Download
This norm can be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself. A seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm, but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. [1] A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space.
Derivative of norm of function w.r.t realpart of function
How to find the derivative of a norm? Derivative a Norm: Let us consider any vector v → = ( v 1, v 2) in R 2 Then the ℓ 2 norm of the given function is represented as: ‖ v → ‖ = v 1 2 + v.
[Solved] Derivative of Euclidean norm (L2 norm) 9to5Science
derivatives - Differentiation of vector norms - Mathematics Stack Exchange Differentiation of vector norms Asked 10 years, 11 months ago Modified 7 years, 9 months ago Viewed 50k times 15 I want to solve the following equation ∂ ∂β[||y −Xβ||2 +||β||2] = 0 ∂ ∂ β [ | | y − X β | | 2 + | | β | | 2] = 0 for β β.

Derivative by First Principle Brilliant Math & Science Wiki
Differentiation of norm Asked 8 years, 3 months ago Modified 2 years, 11 months ago Viewed 12k times 2 How do I differentiate the "norm" of (x −μ) ( x − μ), with respect to μ μ, where both x x and μ μ are vectors ? How will I start and proceed ? Thank you in advance. derivatives normed-spaces Share Cite Follow asked Sep 8, 2015 at 7:26
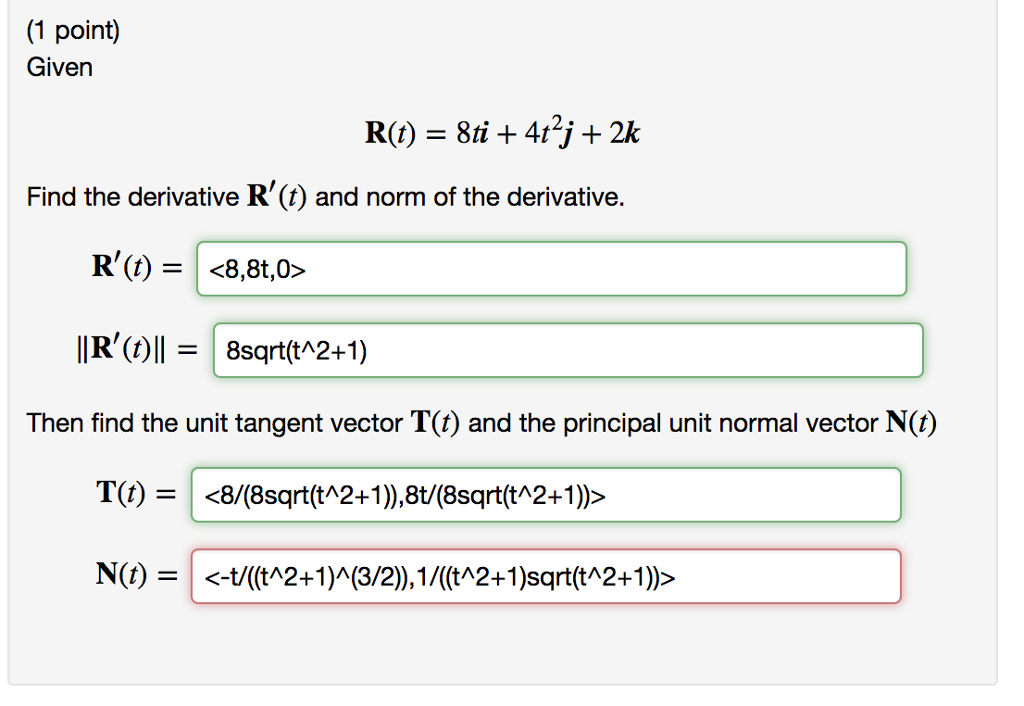
Solved (1 point) Given Find the derivative R'(t) and norm of
One way to approach this to define x = Array [a, 3]; Then you can take the derivative x = D [x . x, {x}] and you'll get more what you expect. Otherwise it doesn't know what the dimensions of x are (if its a scalar, vector, matrix). - bill s. Apr 11, 2021 at 20:17. Thanks, now it makes sense why, since it might be a matrix.

Derivative of the 2norm of a multivariate function YouTube
This notion of derivative is a generalization of the ordinary derivative of a function on the real numbers since the linear maps from to are just multiplication by a real number. In this case, is the function Properties A function differentiable at a point is continuous at that point.